Does Boric Acid Treat Vaginal Yeast Infections?

The Bottom Line
Boric acid has antibacterial and antifungal properties, and boric acid suppositories are used by some women to treat vaginal yeast infections. The suppositories are meant to be inserted directly into the vagina, and should not be swallowed. Consumption of large amounts of boric acid may result in gastrointestinal distress, kidney problems, or death.
What is boric acid?
Boric acid is a chemical that contains the elements boron, oxygen, and hydrogen. Both boric acid and borax contain the element boron, but have distinct formulas and different chemical structures. Boric acid and borax are used in foods, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical products as preservatives and buffering agents.
What is boric acid powder used for?
Boric acid powder is an ingredient in some ant and roach killers. Boric acid is believed to kill insects by damaging their intestines and nervous systems. Certain types of cockroaches can be killed after either consuming boric acid powder or having external contact with the powder. While boric acid is poisonous to many cockroaches, it may be less effective in killing other types of nuisance insects, including bedbugs.
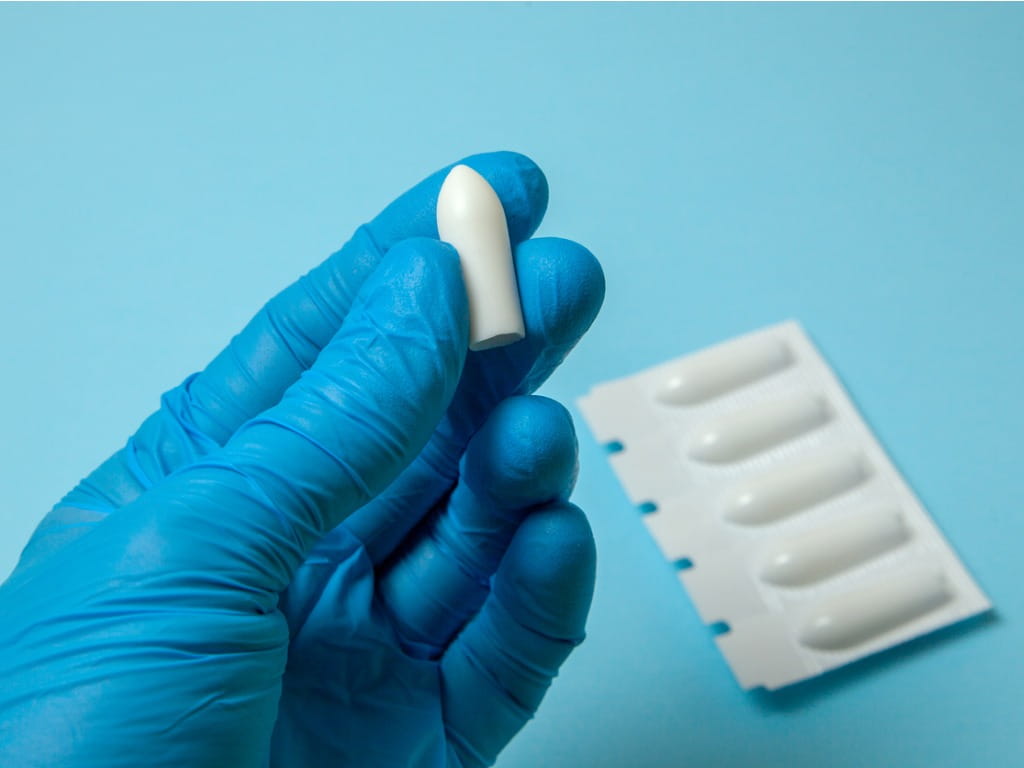
What are boric acid vaginal suppositories?
Boric acid is effective in killing some bacteria and fungi, and has been used as a topical antiseptic agent since the 1800’s. Boric acid suppositories are solid capsules that contain boric acid and are designed to be inserted directly into the vagina. The antifungal effect of boric acid may be enhanced by the acidic vaginal environment, and some studies suggest that boric acid vaginal suppositories may be effective when used as short-term treatments for vaginal yeast infections. When used as a suppository, boric acid is not absorbed significantly into the bloodstream, and significant toxicity is therefore unlikely to occur.
How do you use boric acid suppositories?
Boric acid vaginal suppositories are frequently used as a short-term remedy. Because these products are not approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration, there is no standard recommended dose of boric acid vaginal suppositories. In some studies, regimens of 600 mg once or twice daily for fourteen days have been used. Boric acid vaginal suppositories are not meant to be taken by mouth. Instead, these suppositories should be inserted directly into the vagina.
What are the side effects of boric acid suppositories?
After short-term use, side effects of boric acid suppositories may include a burning sensation in the vagina, watery vaginal discharge, and vaginal redness. Sometimes, male sexual partners may experience a painful sensation during sexual intercourse with women who use boric acid suppositories. There is little published information on the safety of long-term use of boric acid vaginal suppositories.
Have there been deaths from boric acid suppositories?
In humans, boric acid consumption can result in vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. In severe cases, lethargy, kidney failure, and death may occur. Boric acid suppositories typically contain smaller amounts of boric acid that are unlikely to cause significant toxicity in humans when swallowed, and because of this it is unlikely that consumption of a boric acid suppository by an adult will result in serious poisoning or death.
Can pregnant women use boric acid suppositories?
The safety of boric acid vaginal suppositories has not been extensively studied in pregnant women. In addition, the potential effects of boric acid exposure on fetal development have not been fully investigated. For these reasons, pregnant women should avoid using boric acid vaginal suppositories.
What should I do if I swallow a boric acid suppository?
If you or a loved one swallows a boric acid suppository or has worrisome side effects after using a boric acid suppository, get guidance from Poison Control immediately. Help from Poison Control is available at www.poison.org and by phone at 1-800-222-1222. Both options are free, confidential, and available 24 hours a day.
Kelly Johnson-Arbor, MD
Medical Toxicologist
For media inquiries, please contact Krista Osterthaler at osterthaler@poison.org.
Poisoned?
Call 1-800-222-1222 or
Prevention Tips
- Keep all medications, including over-the-counter products, well out of reach of young children.
- Talk to your doctor if you experience frequent or recurrent vaginal yeast infections.
- Seek medical attention if you have pelvic pain, vaginal bleeding, or if you are pregnant.
This Really Happened
A 32-year-old HIV-positive woman experienced recurrent vaginal yeast infections despite long-term treatment with prescription medications including fluconazole, itraconazole, nystatin, and gentian violet. After she began using topical lanolin ointment and boric acid vaginal suppositories, her symptoms quickly resolved within 24 hours. She used the suppositories for ten days and had no reported side effects. Blood testing performed during the ten-day treatment course failed to detect any boric acid within her bloodstream, suggesting that the use of the suppositories was unlikely to result in systemic boron toxicity.For More Information
References
Siegel E, Wason S. Boric acid toxicity. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1986 Apr;33(2):363-7.
Poisoned?
Call 1-800-222-1222 or
Prevention Tips
- Keep all medications, including over-the-counter products, well out of reach of young children.
- Talk to your doctor if you experience frequent or recurrent vaginal yeast infections.
- Seek medical attention if you have pelvic pain, vaginal bleeding, or if you are pregnant.
